http 1.0 http 1.1
HTTP1.0最早在网页中使用是1996年,那个时候只是使用一些较为简单的网页和网络的请求,每次请求都需要建立一个单独的连接,上一次和下一次请求完全分离。这种做法,即使每次的请求量都很小,但是客户端和服务端每次建立TCP连接和关闭TCP连接都是相对比较费时的过程,严重影响客户端和服务端的性能。
基于以上的问题,HTTP1.1在1999年广泛应用于现在的各大浏览器网络请求中,同时HTTP1.1也是当前使用最为广泛的HTTP协议(2015年诞生了HTTP2,但是还未大规模应用),这里不详细对比HTTP1.1针对HTTP1.0改进了什么,只是在连接这块,HTTP1.1支持在一个TCP连接上传送多个HTTP请求和响应,减少了建立和关闭连接的消耗延迟,一定程度上弥补了HTTP1.0每次请求都要创建连接的缺点,这就是长连接,HTTP1.1默认使用长连接。
那么,长连接是如何工作的呢?首先,我们要明确一下,长短连接是通信层(TCP)的概念,HTTP是应用层协议,它只能说告诉通信层我打算一段时间内复用TCP通道而没有自己去建立、释放TCP通道的能力。
- http的keep-alive和tcp的keep-alive的区别
- http的keep-alive是为了复用已有连接
- tcp的keep-alive是为了保活,即保证对端还存活,不然对端已经不在了我这边还占着和对端的这个连接,浪费服务器资源,做法是隔一段时间发送一个心跳包到对端服务器,一旦长时间没有接收到应答,就主动关闭连接
WebSockets
WebSockets provide a persistent connection between a client and server that both parties can use to start sending data at any time.**
1 | // Create a new WebSocket. |
Once the connection has been established the
openevent will be fired on your WebSocket instance.请求
ws://localhost:9095/webSocket/d72b3660-29a8-4276-9eb1-3373e82fdd92后台请求的结果传入websocket是通过session建立关联的
SSE(Server-Sent Events)
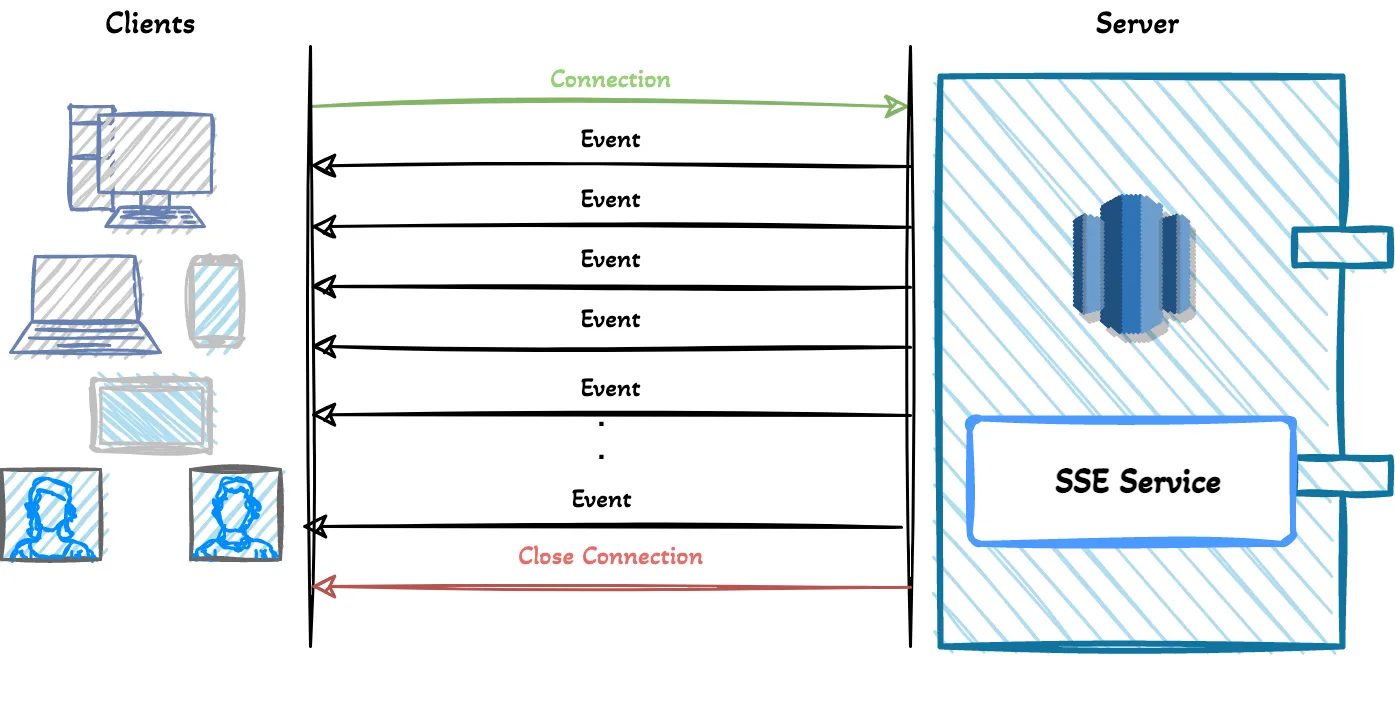
client
1 | GET/POST /api/v1/live-scores |
Accept: text/event-streamindicates the client waiting for event stream from the server,Cache-Control: no-cacheindicates that disabling the caching andConnection: keep-aliveindicates the persistent connection. This request will give us an open connection which we are going to use to fetch updates. After the connection, the server can send messages when the events are ready to send by the server. The important thing is that events are text messages inUTF-8encoding.
1 | curl -H "Accept: text/event-stream" -H "Cache-Control: no-cache" -N <SSE_ENDPOINT_URL> |
server
Disadvantages
- One potential downside of using Server-Sent Events is the limitations in data format. Since SSE is restricted to transporting UTF-8 messages, binary data is not supported.
- When not used over HTTP/2, another limitation is the restricted number of concurrent connections per browser. With only six concurrent open SSE connections allowed at any given time, opening multiple tabs with SSE connections can become a bottleneck. (Credit: Dan Messenger)